Climate changes, as one of the biggest threats to a global food security, highly influence natural resources that are essential for crop production. Farming is not only affected by the impact of climate changes, but it’s also a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions. Intensive farm practices that include both farm production and change of land use, directly affect the global carbon, water, and nutrient cycles. Farming, as a direct driver for 80% of global deforestation, also releases significant amounts of greenhouse gasses. Furthermore, as forests continue to be cleared, the land is directly exposed to wind and water soil erosion.
Agroforestry as a Solution
Agroforestry, as the bridge between forestry and farming, is a diversified set of farm production systems that integrates trees in the farms. There are three different types of agroforestry:
- Agrisilvicultural systems; the combination of crops and trees
- Silvopastoral systems; the combination of forestry and grazing of domesticated animals
- Agrosylvopastoral systems; the combination of trees, animals, and crops.
Tree cover on farms has the potential to make an important contribution to climate change mitigation. There are many benefits of incorporating the planting of trees in farm management such as:
- Improve carbon sequestration; during the photosynthesis process, the tree absorbs carbon from the atmosphere. Studies have shown that a tropical tree absorbs about 22kg of carbon each year. By using this practice, farmers can significantly mitigate climate change;
- Reduce soil erosion; farmers who plant trees as a natural barrier could prevent wind or water erosion;
- Improve soil management; deep-rooting trees improve soil stability; trees increase the soil’s ability to absorb and retain water, produce nutrients, improve and maintain organic soil matter and manage soil temperature;
- Trees attract vital pollinators and birds, which supports integrated pest management;
- Improve water management; surface water run-off is reduced, trees protect nearby water courses by trapping farm pollutants; trees capture, filter, and store water and manage water supplies
- Provide shelter and shade for livestock and crops
- Lessen the risk of salinization
- Provide additional revenue or food for farmers who grow trees that produce fruit, nuts or leaves
- The felled trees or their residues can be used as a firewood
- Leaves can serve as a fodder for livestock
- Certain trees are an important source of natural remedies.
Often underestimated, forests and trees make an essential contribution to global food security. The following picture gives you a brief overview of agroforestry as a good farm practice that has many advantages in mitigating the climate changes and farm production improvement.
Sustainability of integrating trees in farming
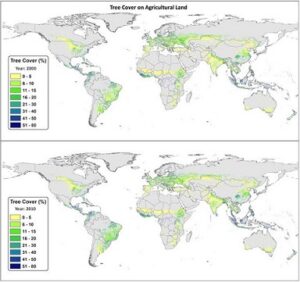
While the size of world’s forest is declining every year, the number of trees on farms is increasing. Studies have shown that 43% of all agricultural land has at least 10% of the total tree cover. Distribution of tree cover is broadly followed by bioclimatic zones; high tree cover is found in humid regions. In the period between 2000 and 2010, the global tree cover increased significantly..
Global tree cover on agricultural land in 2000 and 2010
As the world population continues to grow, farmers are challenged to produce more by using sustainable farm practices that mitigate climate changes. One of the practices that offer a solution for a sustainable food production is the incorporation of trees in farming. Another solution for meeting the food demands of the global population in a sustainable way is AGRIVI farm management software. With a knowledge base for over 100 different crops, AGRIVI provides the opportunity to embrace the best farm practices. With AGRIVI, farmers are able to track all of their activities in a user-friendly way. Powerful analytics and field utilization, together with smart pest alarms are one step towards to sustainable farm production.
Embrace sustainable farm practice, use AGRIVI and leave the mark on the world food production.
Text sources: FAO || Nature || Woodland Trust || FAO
Image sources: Vi Agroforestry || Woodland Trust || Nature