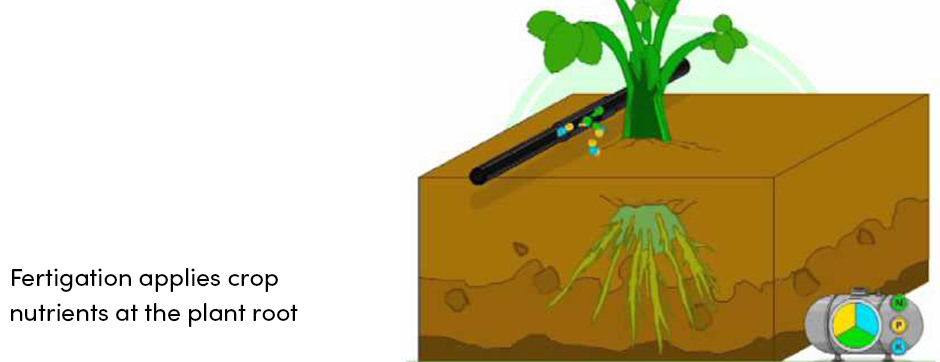
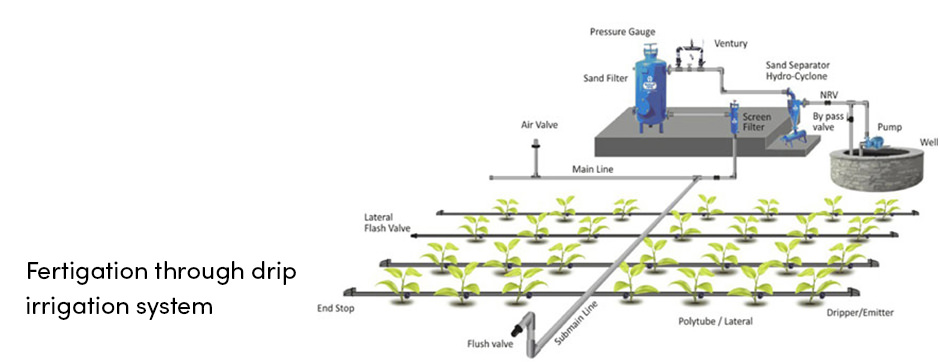
Fertigation is the type of fertilization in which fertilizers are applied through an irrigation system directly to the plant roots. This is the most advanced and efficient fertilization practice. Even ancient farmers have recognized this farm practice as very efficient and useful for successful crop production.
Broadcast fertilization leaves a considerable fraction of the fertilizer on the soil surface. Because of this, the plant is not able to use all of nutrients because they are not in the plant root zone, making them inaccessible. Therefore, fertigation has shown to be a much better practice to fertilize crops.
Fertigation may be practiced under any irrigation system:
- Sprinkler irrigation
- Surface irrigation
- Drip irrigation.
Fertilizers applied with drip irrigation can provide plants with a more uniform nutrient distribution in the field due to more efficient water use.
Moreover, drip irrigation doesn’t wet foliage thus reduces disease occurrence. Additionally, with this type of irrigation, there is no chance of run-off and the possible effects of wind are significantly decreased.
The result is quality crops and high yields, and most importantly, a minimal risk of environmental pollution by plant nutrients.
How Does It Work?
Fertigation is the combination of irrigation and fertilization. To apply fertilizers through the irrigation pipes, special fertilizer injectors must be installed to the irrigation system. This is a simple process that doesn’t require much time.
In fertigation, various nutrients can be added to plants, whether macro- or micronutrients. It primarily depends on the crop type and the crop’s growth stage.
Why Use Fertigation?
Fertigation is a great farm practice that will ensure plants optimal crop nutrition and boost the crop yield, while minimizing environmental pollution. Other benefits of this farm practice include:
- Rational and frequent nutrient supply according to the crop’s needs
- Efficient plant nutrient use
- Nutrient application at the active plant root zone
- Ability for plants to use nutrients immediately after application
- Easy control of timing, amount, and ratio of applied nutrients
- The ability to apply nutrients at any moment; especially when field conditions are not favorable for standard fertilization practices.
Essential Factors to Consider for Proper Fertigation Management
Prior to fertilizing crops through an irrigation system, a farmer needs to consider the following factors which, if not carried out properly, can negatively affect the crop growth and the entire crop production:
Fertilizer selection
- In fertigation, either water-soluble or liquid fertilizers can be used. When choosing a proper fertilizer, crop growth stages should be considered, as well as irrigation system type and water quality.
Fertilizer solubility
- Mixing of two or more fertilizers significantly reduces their solubility. Solubility can be increased with temperature. Fertilizers should be dissolved separately and then added into the water tank.
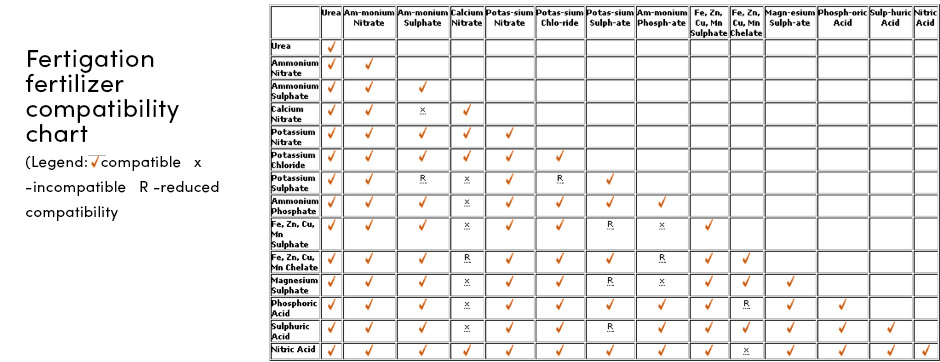
Fertilizer compatibility
- Fertilizer compatibility can affect availability and uptake by the plant, therefore prior to fertilizer mixing a farmer should check their compatibility
Irrigation water pH
- Water pH has a great effect on the availability of residual nutrients in the soil. Hence, irrigation water needs to be within a pH range of 5.5-7.0. Too high of a pH may reduce the availability of essential plant nutrients such as phosphorus, zinc, and iron. On the other hand, a pH that is too low may increase aluminum and manganese concentration in the soil, thus negatively affecting the crop growth.
Fertigation schedule
- In fertigation, accurate fertilizer application greatly determines fertigation management. A fertigation schedule will vary based on crop growth stages and soil properties, along with the irrigation system and climatic conditions.
Disadvantages of Fertigation as a Farm Practice
- A well-designed irrigation system is required to ensure appropriate fertilizer distribution
- The cost for installation of fertilizer injectors on the existing irrigation system
- High labor cost due to frequent fertilizer mixing and applying
- Possible negative effects on plants and soil due to improper use.
Fertigation is a farm practice used worldwide to enhance crop production. It is notable for providing optimum concentrations and quantities of nutrients directly into the plant root zone. Successful fertigation management requires much planning and many factors must be considered prior to fertigating plants. In doing so, a farmer can achieve quality crops and a high yield.
Farming is changing due to the development of improved and modern farm solutions, such as modern fertigation. Therefore, in aiming to enhance the yield and crop production as a whole, farmers have to accept modern farm solutions and change their way of farm management to include elements that are more efficient and sustainable.
Text sources: International Potash Institute || Christmas Tree || Research Gate
Image sources: GOKUL PLAST || You Tube || Sujai Rigation || Engormix