Biofertilizer contains living microorganisms that, when applied to soil, colonize the rhizosphere or the interior of the plant and promote growth by increasing the availability of primary nutrients to the host plant. They encourage plants to absorb, on their own, a greater quantity of nutrients which, even if they are naturally present in the soil, on occasions cannot be assimilated by plants because they are in an insoluble form. Conventional chemical fertilizers, however, supply the soil with chemical elements which, despite functioning as a fertilizer, can end up contaminating aquifers if they are not managed in the right dose and at the right moment.
Types of Biofertilizers
The various types of biofertilizers which help the plant to grow at different levels of its growth are:
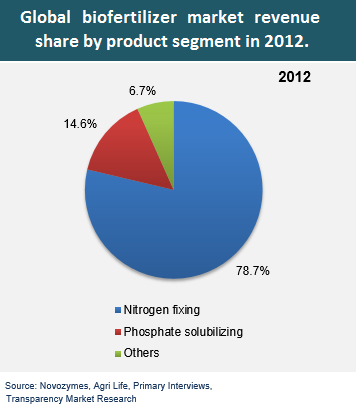
- Nitrogen-fixing biofertilizers (Azotobacter, Nostoc, Rhizobium, Azospirillum)
Increase soil nitrogen level ii. Fixes the atmospheric nitrogen in the soil and make it available to the plants
- Phosphate biofertilizers
Phosphorous solubilizing biofertilizers (Species of Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Penicillium, Aspergillus)
Solubilize the insoluble phosphate from organic and inorganic phosphate sources, releases insoluble phosphorus in soil and fix in clay minerals, secrete organic acids and lower the pH to dissolve bound phosphates in soil
- Phosphorus mobilizing biofertilizers (Arbuscular Mycorrhiza, AM fungi)
The fungus penetrates the cortical cells of the roots, increase the surface area of roots, displace of absorption equilibrium of phosphate ions which increases the transfer of P ions, stimulate metabolic processes, Arbuscles absorb these nutrients into the root system
- Biofertilizers for micro-nutrients (Bacillus sp.)
Bacterial species are Silicate and Zinc solubilizers, degrade silicates and aluminum silicates in soil, help in silicate weathering
- Plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria ( Pseudomonas sp., Bacillus sp.)
Act as both biofertilizer and biopesticides, promote growth by improved nutrient availability (biofertilizers), suppression of plant disease (bioprotectants), phytohormones production (biostimulants)
- Compost (Cellulolytic fungi, Azotobacter)
Utilize animal dung to enrich the soil with microorganisms, eco-friendly organic fertilizer, consists of nitrogen, phosphate solubilizing bacteria and various decomposing fungi, microorganisms breaks down organic matter (dead plants, farmyard waste, cattle waste)
Liquid Biofertilizers
Liquid biofertilizers are suspensions having agriculturally useful microorganisms, which fix atmospheric nitrogen and solubilize insoluble phosphates and make it available for the plant. It reduces the use of chemical fertilizer by 15-40%, has long shelf life, and it’s easy to produce and apply. Also, it helps to produce and manage organic crops so as to compete in the global market.
Learn more about biofertilizers and other modern farming technologies with the help of AGRIVI farm management platform. Get a demo today and start improving your production immediately!