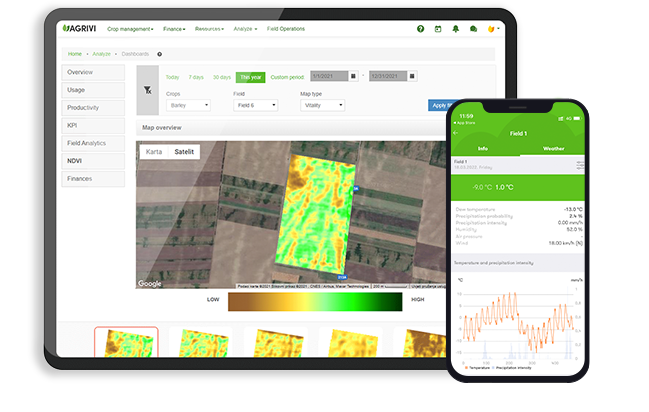
Like every other living organism, plants are susceptible to diseases. Crop disease involves any harmful deviation or alteration from the normal functioning of the physiological processes. Therefore, diseased plants suffer disturbances from normal life processes and their vital functions.
In an attempt to reach high yields and healthy crops, farmers throughout the world struggle to prevent and eradicate various diseases from their crops. Each crop is susceptible to particular diseases that affect the quality and final yield potential.
Generally, it’s estimated that various pests (insects, weeds, nematodes, animals, diseases) each year cause crop yield losses of 20-40%. More precisely, there is some data that maintains that crop diseases cause average yield losses of 42% for the most important food crops. In some cases, crop diseases destroy the whole crop production.
For this reason, it’s extremely important for farmers to find out all they can about the crop diseases so they can manage them properly.
What Causes Crop Diseases?
The disease usually occurs and spreads from season to season, depending on the presence of a certain pathogen, as well as environmental conditions and the characteristics of each crop variety. Essentially, crop diseases occur according to the nature of their causal agent:
- Abiotic or Noninfectious disease agents
- Biotic or Infectious disease agents.
Abiotic, or Noninfectious disease agents, include non-living environmental conditions or inappropriate farm management. They are not transmissable to other plants. A few universally recognized abiotic agents are:
- Extreme temperatures
- Moisture
- Wind
- Frequent and heavy rain
- Drought or flood
- Excess or deficiency of nutrients
- Soil compaction
- Chemical injury caused by pesticides or salts
- Improper water management
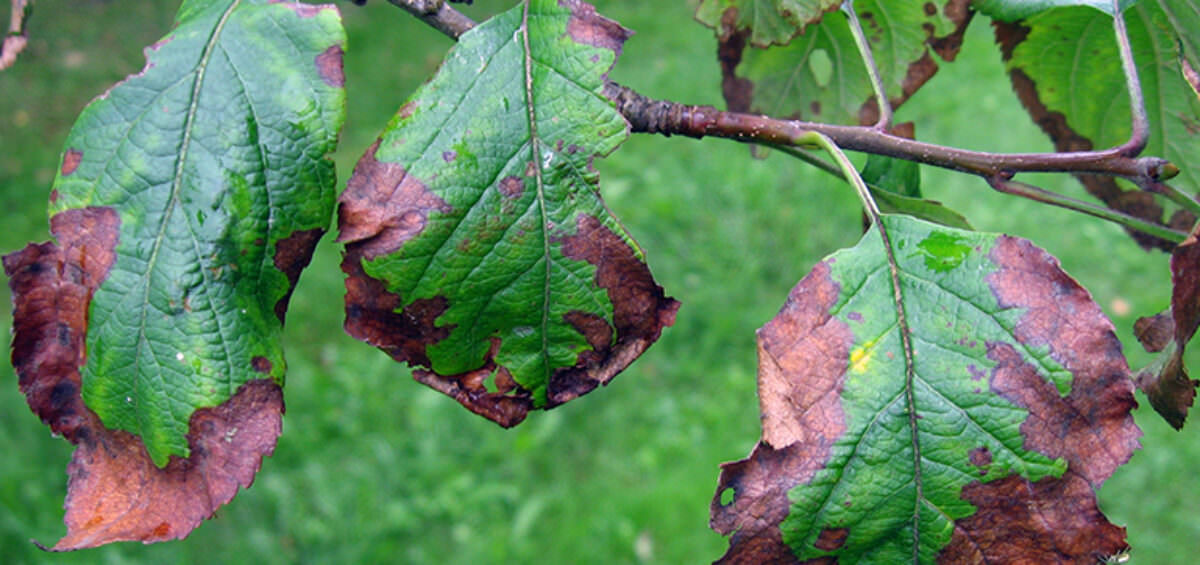
Biotic, or Infectious disease agents, are living organism pathogens capable of spreading from one host to another and transmitting the disease.
The pathogens are classified as:
- Fungi; the most common pathogens, cause around 85% of plant diseases; examples include Black or stem rust caused by the fungus Puccina graminis tritici
- Viruses; are transmitted by a vector or attack the plant through a wound; for example, the Apple mosaic virus affects apple, plum, and hazelnut,
- Bacteria; mutate and multiply rapidly; they enter the plant through a wound or stomata; for instance, the Apple fire blight is caused by Erwinia amylovora
- Nematodes; damage the crops causing galls on roots
- Parasitic plants, live on crops, as they lack chlorophyll they obtain it from the host plant; for example, the dwarf mistletoe grows on other plants and derives nutrients from the host
- Algae; theoretically don’t cause significant damage, however, the may under special circumstances
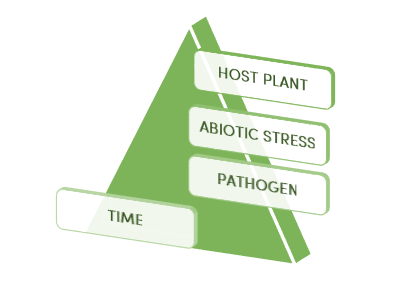
How Disease Occurs in the Plant
Understanding the disease and the development process is the first step towards successful disease management. There are a few special conditions that are conducive for disease development. First, each crop is susceptible to some disease. Second, abiotic factors, namely weather, weaken the plant significantly. Therefore, the plant is vulnerable to the attack of the pathogen. So, the pathogen acts like a cherry on top. When all of the aforementioned factors (susceptible crop, abiotic stress, pathogen attack) are present together and at the same time, disease occurs. That is called the Plant Disease Pyramid.
Plant disease pyramid
How to Save the Yields and Quality of Crops?
Saving the yields and protecting the crops from diseases is a burning issue for every farmer who wishes to see the best results. From the beginning, the first and crucial step in crop protection is knowledge. Every farmer should be aware of susceptibility of the crop to certain diseases, as well as the abiotic agents that are favorable for the occurrence of the disease.
More importantly, one of the most powerful practices is practicing preventative measures, such as:
- Planting resistant varieties
- Managing optimal planting and harvesting times
- Planting healthy and quality material
- Dezinfestation of equipment
- Crop rotation
- Managing plant nutrients according to crop needs
Outside the preventative measures, there are also a few curative measures that should be taken in the case of the disease actually occurring. These measures include:
- The using of various chemicals, including fungicides, nematicides, bactericides, algacides
- Removing infested plant parts
- Utilizing various beneficial predators such as viruses, fungi, or bacteria.
There is one additional thing that could make a significant difference in disease farm management. Regular monitoring of crops and fields, as well as on-time reaction, can be a true lifesaver for every crop production.
Text sources: MDPI || Colorado State University
Image sources: Iowa State University || Queensland Government || eXtension