The soil; A primary resource for food production and the most important tool for every farmer. Successful farming depends on the quality of soil, which provides water and essential nutrients to crops. Rich and healthy soil, combined with the appropriate amount of water and sunlight can significantly contribute to a successful farming season and meeting yield quotas.
Proper soil management protects and enhances soil performance. It also reduces input costs, prevents pollution, and improves crop quality. Before planting, the soil should be in the best physical condition for the crop, to encourage rapid and successful root growth. All crops have different soil requirements, but there are a few common practices that could encourage healthy soil biology.
Table of Contents
Proper Tillage: Preparing The Soil For Growing Crops
Soil tillage is the first and most important activity. It directly affects the final yield and that’s why it needs to be carried out properly. Proper tillage practices can significantly improve the quality and crop yields. The process of preparing the soil for growing crops starts with a soil tillage plan.
During the crop production process, farmers perform several types of soil tillage. These are as follows:
- Undermining or mole drainage—a poorly used tillage practice; mainly to solve standing water and soil porosity problem
- Plowing—classified into very shallow, shallow, and pre-sowing plowing, this practice is the base of soil tillage; it improves soil microbiological activity, destroys already emerged weeds and prevents losses of moisture from the soil by evaporation
- Disking—plays a huge role in preparing the soil for sowing; disking breaks up clods and surface crust, thereby improving soil granulation and surface uniformity
- Harrowing—creates a crumbly layer for planting thus protecting the soil surface from rapid drying and enhancing plant nutrient availability
- Rolling—the final soil tillage practice to create a smooth and firm seedbed and press the seeds into the soil for faster germination
There are various tillage systems, depending on product type, soil condition, crop planted, and farm practices. The following picture summarizes tillage operations for both conventional and conservation tillage.
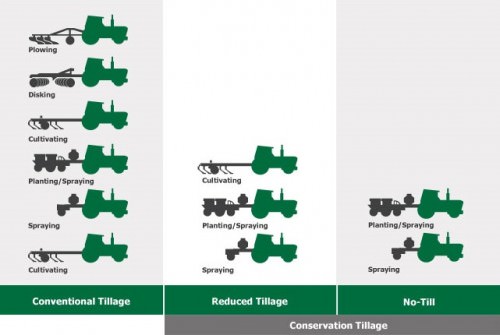
Tillage systems used for crop production
It has a major role in soil management practices carried out before planting. Organic matter improves soil structure, enhances water and nutrient holding capacity, protects the soil from erosion and compaction, and supports a healthy community of soil organisms.
Conventional tillage is full-width tillage that disturbs the whole soil structure and includes various tillage operations before and after crop planting. On the other hand, the reduced and no-till tillage systems minimize soil disturbance and maintain a high level of surface residue.
Successful Soil Management Means Having a Comprehensive Soil Analysis
In order to follow good practices for sustainable soil management, it’s essential that farmers regularly perform soil analysis. By testing their soil, farmers can see the exact amount of soil nutrients, humus content, and pH value. According to the content of nutrients in the soil and the crop requirements, it’s easy to determine the necessary amount of fertilizer to achieve higher yields and fruit or vegetable quality.
The Importance of Organic Matter In Soil
Soil organic matter is the organic component of soil consisting of all living soil organisms and the previous living organisms in their various degrees of decomposition. The three primary parts include small (fresh) plant residues and small living soil organisms, decomposing (active) organic matter, and stable organic matter (humus).
Soil organic matter content can be estimated in the field and tested in a lab to provide estimates for Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulfur mineralized available for crop production and adjust fertilizer recommendations. Soil organic matter impacts soil quality and is an important factor in maintaining sustainable agriculture practices.
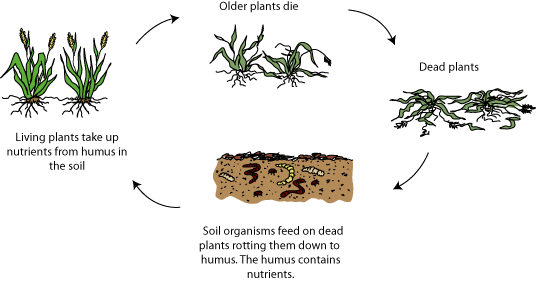
The formation and role of organic matter in the soil
Biological, Physical, and Chemical Soil Protection Measures
In order to minimize crop damage created by pests and maintain soil health, farmers apply different protection measures: crop rotation, crop isolation, tillage, mixed farming, proper planting time, cover crop and barriers, mulching, row maintenance in orchards, and green manure, chemical, and natural soil and plant treatments. Check out our post on the best practices for pest management here.
Proper Drainage and Irrigation
It is important to ensure good soil drainage, aeration, and optimum humidity for young plants. Soils with less drainage may accumulate higher amounts of water than is needed and thus negatively affects plant growth. In fields where the water is insufficient, placing irrigation equipment is required. Immediately after planting and during the first stages, irrigation is a crucial farm practice. By following these practices, farmers can adjust the water needs according to the crop requirements.
Without fertile and nutrient-enriched soil, water quality and soil testing farmers’ efforts in farming would be futile. As a person involved in the food production process, a farmer needs to understand soil requirements and follow agronomic best practices before planting. In addition to these five main practices, Agrivi software can also help farmers to get the best out of their fields.
Use Farm Management Software For Proper Soil Management
With AGRIVI Farm Management Software, farmers can plan their crop rotation, keep soil analysis records, and perform crop management, including tillage, fertilization, pest protection, and irrigation. The software also guides you on how to prepare the soil for planting by giving you best practice processes in the form of tasks for over 80 different crops, for all types of production.
To prepare your soil for planting, use these five practices together with AGRIVI software. Contact us to learn more about how AGRIVI helps optimize your farm operations.