Agriculture of today is faced with many problems. The lack of available farmland, limited access to water, climate change, and overpopulation all jeopardize the overall sustainability of farm production. In aiming to produce enough food for the growing population, farmers are forced to increase crop productivity per field unit. So here is the big question that every struggling farmer is faced with: How this can be achieved? Luckily, there is one possible and quite simple solution: the introduction and use of modern technologies in agriculture. New modern technologies not only bring revolutionary changes into farming but also revolutionize the way in which farmers work.
Modern farm management relies on many different factors, including sensing methodologies, farm equipment, enhanced seeds, and farm software which facilitates the tracking of a complete farm production from one central location. Modern technology helps farmers obtain accurate information of crop, soil, climate, and environmental conditions.
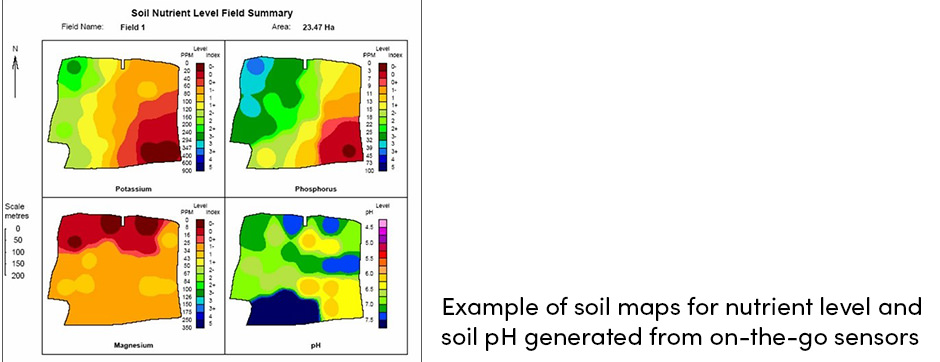
Sensors are important tools in modern agriculture management. They are used either to control variable rate application in real-time or to generate field maps of particular soil properties, in conjunction with GPS.
According to variation in soil characteristics that influence the yield, sensors can measure:
- Soil texture
- Soil moisture
- Soil organic matter
- Soil pH
- Soil nutrient level (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium)
- Cation exchange capacity (CAC)
- Soil compaction
- Pest detection
- Depth of plant roots
- Soil structure and bulk density.
There are two main types of sensors available to farmers for measuring of various soil characteristics. These are:
1. On-the-go sensors
On-the go sensors are sensors attached to a tractor or to its implement which measure various soil characteristics with or without entering the soil. As a tractor with GPS receiver moves across the field, measured data is generated on a soil map. This map can serve as an information for application rate of fertilizers, pesticides or enhancement of soil properties.
2. Real-time sensors
Real-time sensors are sensors attached to a tractor or to its implement which record the real-time changes in the soil, such as nitrogen amount or weed presence. The changes are automatically registered by a central computer which coordinates the application of a fertilizer or herbicide. In this case, a product is applied only where it is needed.
Real-time sensors are generally used for variable-rate application where pesticides, fertilizers, and seeds are applied according to measured soil’s or crop’s characteristics.
Sensors for soil mapping are mainly vehicle-based but can also be made by drones. Soil data is captured on-the-go and instantaneously converted into distribution maps. Based on analyzed data, farmers know which part of the field lacks a certain crop nutrient or need to manage its characteristic. This helps minimize the need for farm inputs use and lower financial cost while increasing crop yield.
Technology is increasingly taking over the agriculture sector. Farmers are not dummy village people anymore, they are becoming technologically educated and proud to participate in eradication of world hunger. Be one of them and reduce the hunger by using modern farm technology.
Text sources: Science Publications || CropWatch
Image sources: LSU AgCenter || Brett Brothers || GeoTecnologie