The beginnings of agriculture reach far back into history. One of the oldest human activities, farming, developed long before the first written documents. However, the exact date of its origin is unknown. Although some archaeological findings confirm that farm production began to develop in the Neolithic period, the latest research by Israeli scientists suggests that agriculture began to develop much earlier, even more than 23,000 years ago. The change from the hunting and gatherer life to the cultivation of plants, domestication of animals, and food production led to the development of the first civilizations of Mesopotamia, Egypt, India and China and further expansion of farm production.


Farm production through history – farming then and now
Farm Production in the World
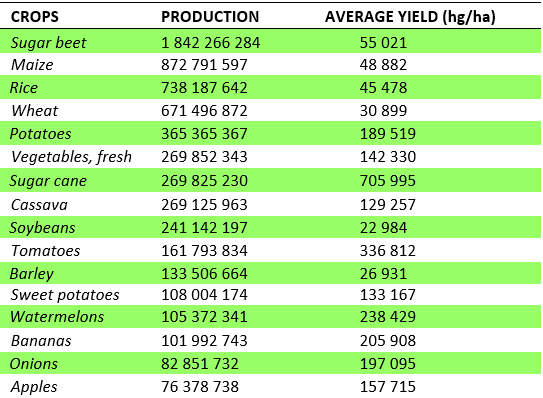
The world’s land area totals 13.958 million hectares, of which 4.992 million hectares are classified as agricultural land. This accounts for about 36% of the total land area. The agricultural land is divided into 3 categories: arable land (28%), permanent crops (3%), and meadows and pastures (68%). The most common type of agricultural production is farming. Grains, such as wheat, rice, barley, and corn, make up the majority of the world’s crop production. Some of the world’s major crops and their production volumes are shown in the following table.
The world’s major crops with their global production and average yield (1 hg = 0.1 kg)
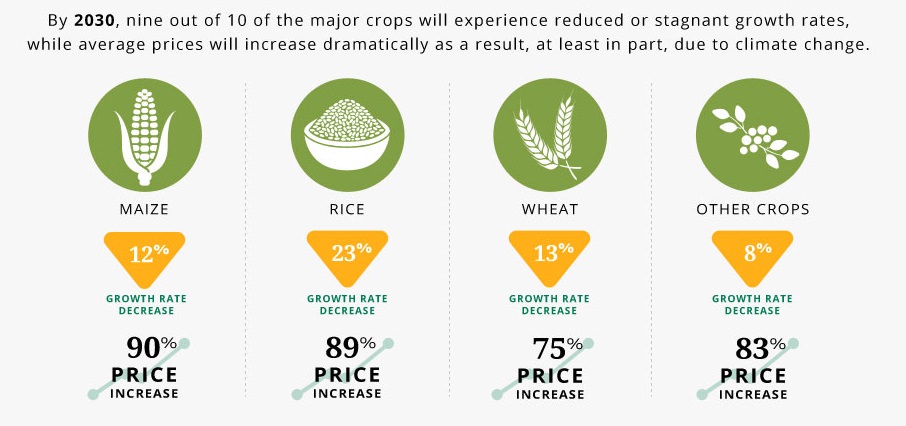
Farm production poses a number of challenges for farmers around the world. Food production requires adjustments to rapid population growth, the expenditure of resources, soil degradation, reduced utilization of land and a growing lack of water. In order to meet current and future needs of a growing world population, it’s necessary to increase farm production. However, this must be done in a sustainable and qualitative way in order to respond the environmental and food safety requirements. Climate changes are yet another of the challenges for today’s farmers, who are forced to adjust their production to increasing risks from weather extremes (such as hail, drought, heavy rain, and soil erosion). Climate changes are not only responsible for adverse weather conditions, they also cause the instability in farm commodity prices.
Impact of climate change on crop production
Farm Production in Croatia
Unlike most countries, Croatia has a wealth of natural resources. Favorable agro-climatic conditions and the diversity of climate, relief, and soil are excellent for the growing of various crops. Croatia is is characterized by a large number of products in a variety of geographical locations in relation to its small area. A diversified rural landscape, natural beauty, and a great number of local products are also suitable for the development of rural tourism. Despite these advantages, Croatian agriculture is faced with problems such as the high rate of food product imports in relation to exports, inadequate farm size, fragmentation of farmland, technological backwardness, abandonment of villages and an aging rural population. Growing social inequality is also still one of the challenges of Croatian agriculture, making it difficult to achieve competitiveness for small family farmers.
A Strategy to Enhance Farm Production
Although agricultural production is facing serious global risks, solutions are possible within the framework of the monitoring and analysis of the risk themselves, and in the context of sustainable agricultural practices. AGRIVI farm management software helps farmers to monitor complete farm production and also facilitates the management of potential farm risks. The software provides the best farm practices for over 100 different crops and allows farmers to monitor all field activities; from the consumption of fertilizers, pesticides, work hours of workers and machinery, to finance monitoring and the powerful analysis of the entire farm production.
Enhance your farm production, start using AGRIVI now.
Text sources: FAO || Huron County View || Encyclopedia Britannica
Image sources: Centery Farm || Tackk || Bell Banks || Farming First || Faostat