Coffee is one of the most important cash crops, known best for its delicious taste. Carefully roasted beans are manufactured to produce popular beverages that are consumed worldwide. Coffee beans are grown along the Equatorial zone called “The Bean Belt”, in over 70 countries. World coffee production is estimated to have produced 155 million 60-kilogram bags, with that figure rising annually. Over 50 percent of total production comes from just four countries, including Brazil, Vietnam, Columbia and Indonesia.
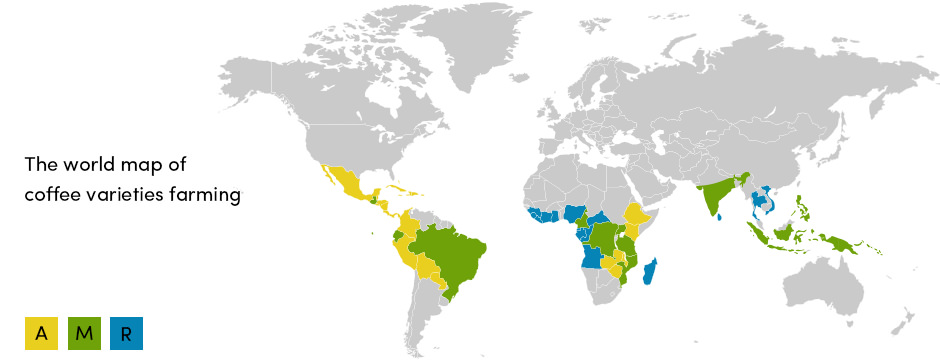
There are many different coffee varieties, with two types most commonly farmed; Robusta and Arabica. Arabica is known to be of superb grain quality. Robusta, on the other hand, is known to be of a lower grain quality but it is much easier to produce and more resistant to diseases. The world map below shows areas in which Robusta and Arabica are grown, as well as areas of mixed production.
Approximately 125 million people worldwide depend on coffee to support and maintain their livelihoods. It is the most valuable and widely traded tropical agricultural product, with 25 million smallholder farmers producing 80% of the world’s coffee.
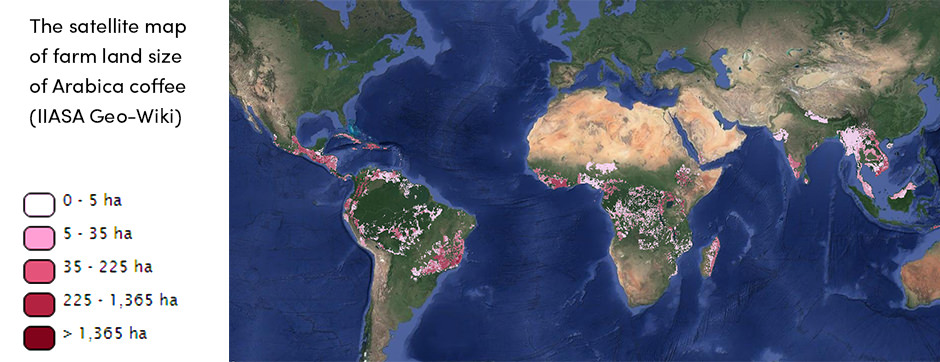
Global coffee production varies from year to year according to weather conditions, diseases, harvest time, and other factors, resulting in a market that is inherently unstable and characterized by wide fluctuations in price. This price volatility has significant consequences for those who depend on coffee for their livelihood. The inconsistency can make it difficult for growers to predict their income for coming seasons and budget for their household and farming needs. Another fact that greatly affects smallholders is the size of the farming area. These farmers often produce coffee on only 1-2 ha of land, which, depending on circumstances, may not always allow production for the planned yield needed to pay off all farming dues.
Coffee farm production is straightforward. There are a few practices that every farmer must apply in order to produce a successful harvest and maintain efficient and effective farm production. Suggested practices are as follows:
- Choose a proper variety for a certain growing area
- Plant disease-free transplants
- Intercrop with vegetables and other fruit trees for maximum land utilization
- Execute on-time and regular insect pest and disease protection
- Administer proper fertilization management (apply only recommended fertilizer dosages for certain varieties)
- Arrange for timely bean harvesting
- Implement a sustainable farm management system.
In coffee production, sustainable farm management practices are extremely important, both to ensure the protection of the environment as well as to reduce climate change due to pollution. In some countries, these farm practices have already been adopted. Such practices as intercrop rotation, use of natural fertilizers and chemicals, reuse of coffee husks as heating fuel, solar coffee dryers, and using renewable resources should be integrated whenever possible.
A sustainable farm gradually adds natural nutrients to the soil by spreading fertilizers and organic matter (composted coffee pulp) under and between the trees. This type of fertilization has been found to increase yields over time and produce a more uniform and natural mineral content in the ground. Another sustainable practice is appropriate water use. Water from fermentation tanks should never be returned to rivers or lakes, but rather filtered naturally through the earth and then used for irrigation.
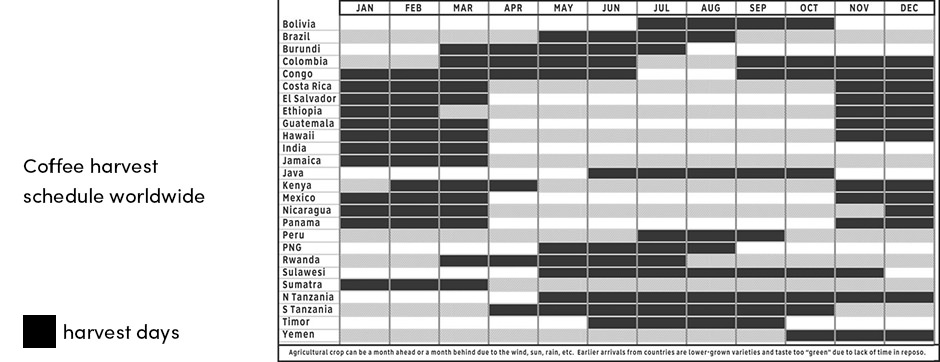
Since coffee is produced throughout many countries worldwide, it is available all year round due to different times of harvest.
Along with following all suggested farm practices, modern farm software and technologies can also be of great importance and serve to be very beneficial to farmers. These software and technologies have the ability to help improve coffee production, achieve higher yields, and track the product through all of its production stages, from processing to distribution.
Text and image sources: United States Department of Agriculture || Fairtrade Foundation || Fairtrade || Coffee Research || Cafe Imports